Key Terms colony. Why culture bacteria in the laboratory.
Luria broth LB is a nutrient-rich media commonly used to culture bacteria in the lab.
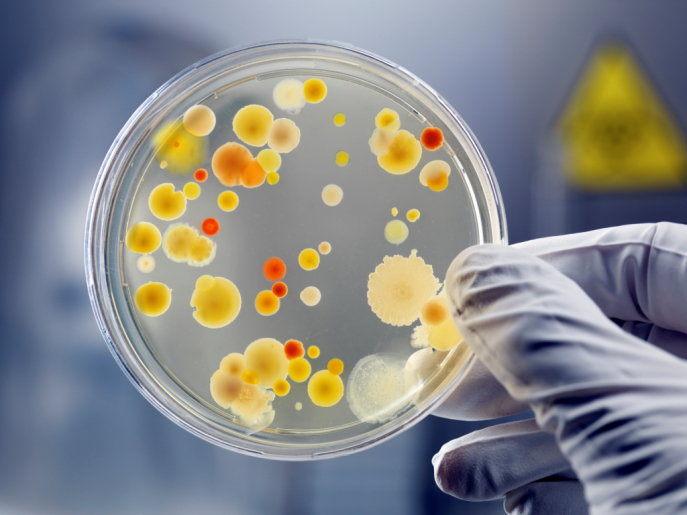
Bacterial culture plate. The ideal temperature for growing bacteria is between 70 98 degrees F 20 37 degrees C 37 o C. LB agar plates are frequently used to isolate individual clonal colonies of bacteria carrying a specific plasmid. A bacterial colony is defined as a visible cluster of bacteria growing on the surface of or within a solid medium presumably cultured from a single cell.
Colonies are small pin-point 05-10 mmcircularsemi-transparent with an area of clear hemolysis β-haemolysis around them Virulent strains on fresh isolation produce matt finely granularcolonies. The Petri dish a circular flat dish with a lid that is used for growing bacteria on a. To insure a countable plate a series of dilutions should be plated.
Medium Water Salts-osmolarity and nutrients Source of carbon-sugars alcohols. In order to ensure a pure culture is being preserved pick a single colony of the bacteria off a plate grow it overnight in the appropriate liquid media and with shaking. From one end of the parallel streaks streak four more parallel lines 90q to the original set.
The elevation of Saureus colony in blood agar is convex while the elevation of this bacterium in nutrient agar is flat. Here the bacteria gain receive nutrients from the agar concentrate. The inoculum is streaked over the agar surface in such a way that it thins out the bacteria.
Allowing for the isolation of individual colonies for counting or further experiments. The pour plate method of counting bacteria is more precise than the streak plate method but on the average it will give a lower count as heat sensitive microorganisms may die when they come contact with hot molten agar medium. To isolate a single species to isolate a single genetic clone of a particular species to isolate a mixed culture of many species.
Spread plates allow for the even spreading of bacteria onto a petri dish. Bacteria culturing is carried out for a plethora of reasons including. Once the growth medium in the petri dish is inoculated with the desired bacteria the plates are incubated at the optimal temperature for the growing of the selected bacteria for example usually at 37 degrees Celsius or the human body temperature for cultures from humans or animals or lower for environmental cultures.
After the desired level of growth is achieved agar plates can be stored upside down in a. Dilute the bacteria on the plate in order to isolate single colonies. 2Streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes On Blood agar.
Bacterial plant maize canola mammalian yeast. Bacterial cultures the plate what it contains and temperatures vary depending on the bacteria and needs. Streak plate method II.
Take the overnight culture and and mix an aliquot with 40 glycerol in sterile water and place in a cryogenic vial. In winter time you may place agar plates close to a radiator heater but dont. For example one type of agar plate culture involves the use of blood as well as heat.
What do we need to successfully culture bacteria in the laboratory. A culture plate 1887 Some of the best inventions seem so obvious after the event. Put the nutrient agar plates into a zipper lock bag and keep the plates upside down and place them in a warm and dark place for several days 3 to 7 days depends the incubation temperature.
Streak plate technique is used for the isolation into a pure culture of the organisms mostly bacteria from a mixed population. The elevation is referring to the height the look at the side view of culture plate of the bacterial colony. Bacterial plant maize canola mammalian yeast.