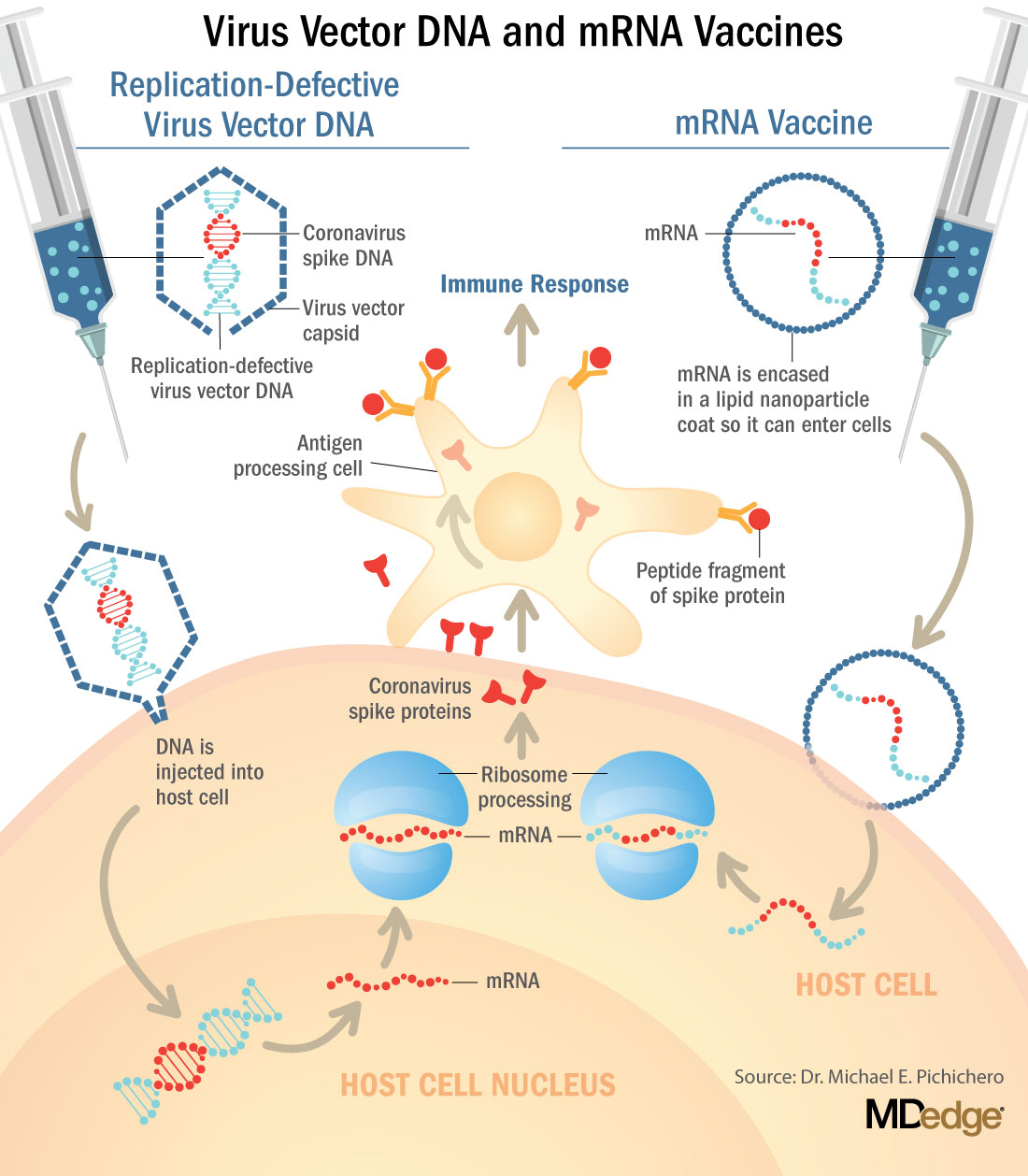
Sarah Gilbert The RNA in a vaccine has to cause the protein to get out of the cell and. Moreover compared to DNA vaccines which could achieve the same thing getting the body to produce the necessary protein antigen RNA vaccines have a definite safety advantage over DNA vaccines.
What an RNA vaccine does unlike most vaccines which are injected with an antigen which is a piece of the target virus a disabled piece and an adjuvant which shocks the body to increase the immune response.

Rna based vaccines. Self-replicating RNA vaccines have displayed increased immunogenicity and effectiveness after formulating the RNA in a cationic nanoemulsion based on the licensed MF59 Novartis adjuvant 50. Results so far have been overwhelmingly positive. Other RNA vaccines in the pipeline include those produced by CureVac Imperial College London and Arcturus.
Once administered and internalized by host cells the mRNA transcripts are translated directly in the cytoplasm and. The Pfizer RNA based COVID-19 vaccine was approved by the US FDA under an emergency use authorization without long term safety data. Nucleic acid vaccines.
These provoke an immune response that allows the body to fight off the actual pathogen later on. The spoils of that investment and the potential success of a PfizerBioNTech vaccine will long outlive this pandemic says Hotez. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are given by injection into the muscle of the upper arm.
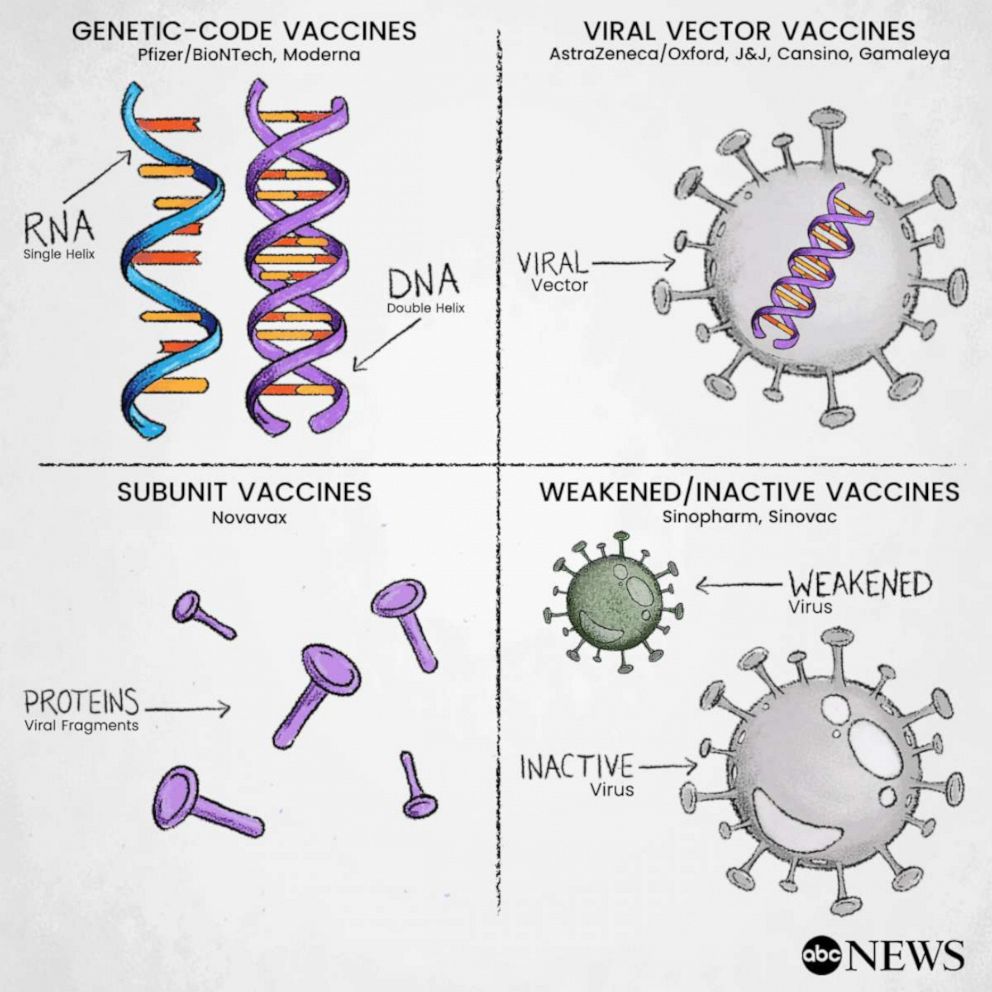
RNA vaccines contain the instructions for making the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Most traditional vaccines consist of either killed or weakened forms of a virus or bacterium. RNA based vaccines offers special risks of inducing specific adverse events.
A wealth of knowledge has been published on a class of RNA binding proteins shown to sic participating in causing a number of neurological diseases including Alzheimers disease and ALS. RNA vaccines are faster and cheaper to produce than traditional vaccines and a RNA based vaccine is also safer for the patient as they are not produced using infectious elements Production of RNA vaccines is laboratory based and the process could be standardised and scaled allowing quick responses to large outbreaks and epidemics. This is an RNA vaccine which has never been made before.
One such potential adverse event is prion based diseases caused by activation of intrinsic proteins to form prions. RNA vaccines traditionally consist of messenger RNA synthesized by in vitro transcription using a bacteriophage RNA polymerase and template DNA that encodes the antigens of interest. Because of concerns about the safety of this vaccine a study was performed to determine if the vaccine could potentially induce prion based disease.
Two vaccines which have recently reported results are RNA vaccines produced by Moderna and by Pfizer BioNTech. This protein is found on the surface of the virus that causes COVID-19. It provides a glidepath for using mRNA technology for other.
Thats how every other vaccine works. RNA-Based Vaccines in Cancer Immunotherapy. With conventional mRNA vaccines entering phase 3 clinical trials for the highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 an saRNA vaccine candidate developed by.
Nucleic acid vaccines consisting of plasmid DNA viral vectors or RNA may change the way the next generation vaccines are produced as they have the potential to combine the benefits of live-attenuated vaccines without the complications often associated with live-attenuated vaccine safety and manuf. RNA is easier and quicker to produce on a mass scale than more traditional protein-based vaccines. Thus the mRNA molecule is essentially a recipe telling the cells of the body how to make the spike protein.
RNA instructs the cell to make the protein and for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines thats the spike protein says Prof. Instead of delivering a virus or a viral protein RNA vaccines deliver genetic information that allows the bodys own cells to produce a viral protein. Brosh compared the mRNA vaccine to traditional vaccines such as those for influenza which use an inactivated virus that was destroyed by heat or.